Unlocking nature's secrets: covellite as a potent abiotic catalyst

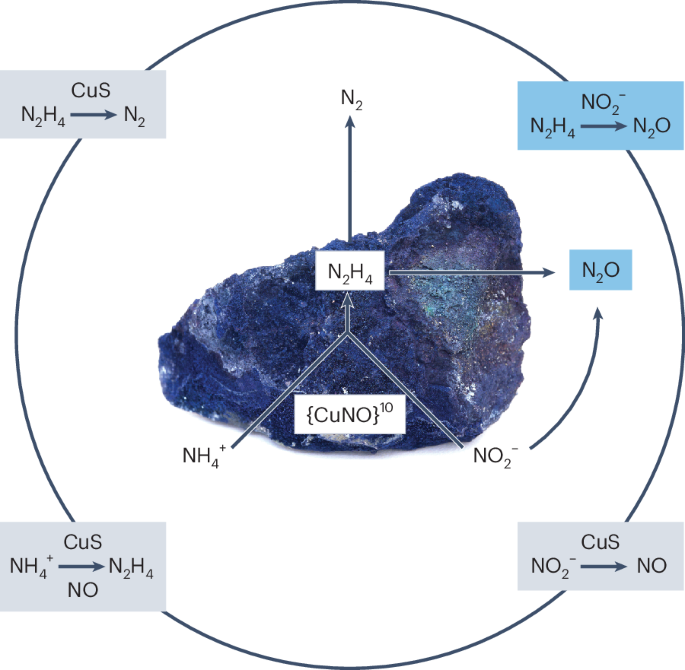
In a world grappling with environmental pollution and the pressing need for sustainable practices, a recent breakthrough in nitrogen cycling unveils an incredible solution. Researchers have discovered that covellite, a naturally occurring mineral, can perform the vital enzymatic conversion of ammonia (NH4+) and nitrite (NO2–) into nitrogen gas (N2). This process, known as abiotic anammox, presents a promising alternative to conventional biological methods, addressing a significant challenge in environmental management and wastewater treatment.
Understanding the Significance of Abiotic Anammox
The enzymatic conversion of nitrogen compounds is crucial for maintaining ecological balance. Traditional methods rely heavily on bacteria, which can be sensitive to environmental changes, making them less reliable in various settings. The discovery that covellite can mimic this enzymatic reaction opens up avenues for more robust, efficient treatment options that can withstand fluctuations in environmental conditions.
What Makes Covellite Unique?
Covellite's ability to serve as an abiotic catalyst is revolutionary. The research showcases how the surface properties and chemical composition of this mineral facilitate the entire anammox reaction pathway. Unlike biological systems, which can be unpredictable, covellite offers a consistent and reliable means to convert toxic nitrogen compounds into harmless nitrogen gas, thereby mitigating nitrogen pollution that poses a threat to both water quality and ecosystem health.
Implications for Environmental Management
This discovery is not just a scientific curiosity—it holds profound implications for wastewater treatment and nitrogen management across the globe. By improving the efficiency of nitrogen removal, we can tackle urban wastewater issues more sustainably, leading to cleaner water bodies and healthier ecosystems. This, in turn, could help combat problems like eutrophication, which often results in dead zones in aquatic environments, drastically affecting biodiversity.
Future Research Directions
The intriguing catalytic activity of covellite necessitates further research to fully understand the mechanisms at play. As scientists delve deeper into the properties that enable covellite to catalyze these reactions, we may see the development of even more efficient abiotic anammox systems. These advancements could lead to scalable solutions for industrial wastewater treatment and even the remediation of polluted sites, providing much-needed relief to toxic environments.
A Vision for a Sustainable Future
In light of these findings, it’s clear that utilizing naturally occurring materials like covellite in environmental applications can significantly enhance our approach to nitrogen cycling. The transition from biological to abiotic systems not only promises improved efficiency but also sustainability, reducing our reliance on fragile bacterial systems.
With continued innovation, the use of covellite and similar minerals could pave the way for cleaner water, healthier ecosystems, and a more balanced nitrogen cycle. As humanity faces the dual crises of pollution and climate change, such discoveries are essential steps toward sustainable solutions, illustrating how looking to nature's own materials can provide the answers we seek for a better future.